Automating Neuronal Cell Immunofluorescence in Microfluidic Chips
In this application note, we introduce the use of Aria, Fluigent’s automated perfusion system, in combination with the M-Switch, to streamline immunolabeling of neuron cells across as many as four microfluidic chips. The automated cell immunostaining process not only expedites procedures but also guarantees consistent preservation of cells with minimal cell damage and no lingering antibody residue, effectively enhancing efficiency and the quality of results.
This application note was produced by Maxime Poinsot, PhD student at the Institut de Neurosciences de la Timone and Fluigent.
Automating Neuronal Cell Immunofluorescence in Microfluidic Chips with Fluigent’s Aria
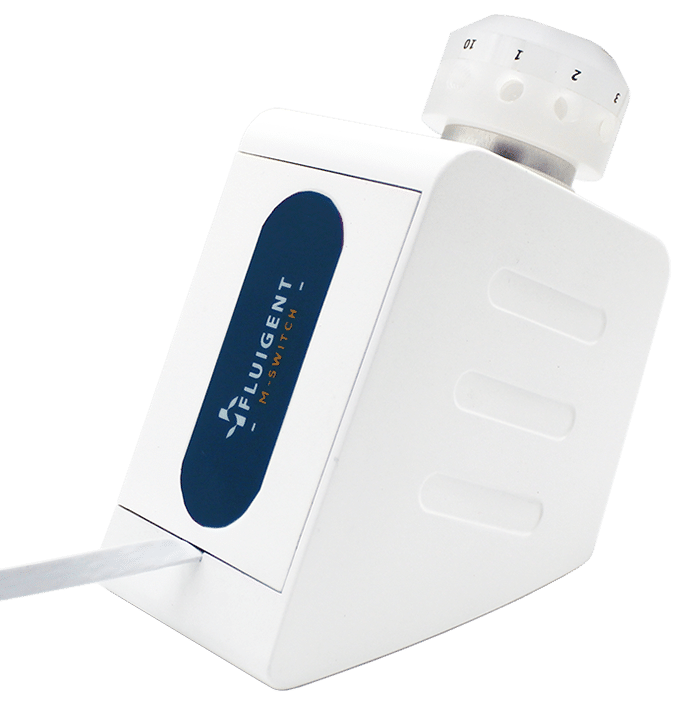
This application note outlines how Aria our automated perfusion system, in combination with the M-Switch 11-port/10-position bidirectional valve, facilitates parallel neuronal cell immunofluorescence of up to four microfluidic chips, allowing up to three different antibodies to be used simultaneously.
By automating the cell immunostaining process, users can significantly reduce the time and effort required while ensuring consistently immunolabeled cells with minimal cell damage and no antibody residue.
Introduction: Microfluidics enhances the efficiency of cell immunostaining
Microfluidic technology has revolutionized the field of cell biology research by providing researchers with unprecedented precision in controlling fluid dynamics at the microscale. Simultaneously, one of the most broadly accepted techniques in biology and biomedical research is immunofluorescence, which plays a pivotal role not only in deciphering protein expression but also in shedding light on the precise cellular or subcellular locations where the studied proteins are active. This versatile technique enables visualization of proteins within cells, whether they are in suspension, adherent to surfaces, in tissues, or even within 3D culture-derived spheroids.
Highly precise, multiplexed, and dynamic cellular analyses are achievable when combining microfluidics with cell immunostaining. However, manipulating cells within the confined dimensions of microfluidic chambers poses a unique set of challenges. When it comes to delicate neuronal cell immunofluorescence, there is an even greater need for meticulous handling to preserve the integrity of axons and dendrites.
The geometric constraints of these microfluidic chambers impose considerable limitations on fluid flow when it comes to perfusing the medium or changing solutions. Cells residing within these chambers are subjected to fluidic stresses that can lead to tearing or detachment of cells from their substrate.
Overcoming the limitations of manual cell immunofluorescence
To overcome these challenges and increase the quality and efficiency of cell immunostaining protocols within microfluidic chips, Fluigent’s automated sequential injection system, Aria, is proposed as an alternative to manual handling. When coupled with the M-Switch, this automated sequential injection system facilitates parallel neuronal cell immunofluorescence in up to four microfluidic chips. By automating the cell immunolabeling process, users can significantly reduce the time and effort required while ensuring consistently stained cells with minimal cell damage and no antibody residue.
This application note is authored by Maxime Poinsot, a PhD student at Institut de Neurosciences de la Timone and Fluigent. The application employs standard reagents, making it accessible and practical for researchers in the field.
Automated neuronal cell immunofluorescence protocol
Materials
Cells & standard immunofluorescence reagents:
- Progenitor neuron cells from rat embryos at 17.5 days of gestation
- Fixation solution: 4% paraformaldehyde PFA in PBS and 1% sucrose in PBS
- Permeabilization solution: 0.1% triton in PBS
- Blocking solution: 0.1% triton, 5% BSA, 2% donkey serum in PBS.
- Primary antibody: Anti-MAP2 mouse in blocking solution 1/800
- Secondary antibody: Anti mouse 488
- Hoechst 1/1000 in PBS to stain the cell nuclei.
Aria serial output:This system is a suitable tool for neuronal cell immunolabeling requiring very precise and gentle fluid perfusion to maintain cell integrity.
Confocal Microscope: Nikon Spinning Disk CSU-W1: The confocal microscope employed, a Nikon Spinning Disk CSU-W1 with a 10x objective, provided high-resolution imaging for neuron cell visualization. A 488 nm laser was used at 70% intensity with a 200 ms exposure time.
Microfluidic chip: The microfluidic chip (Figure 1) used for this application note is a homemade chip, fabricated using PDMS (Polydimethylsiloxane) with a curing agent ratio of 1 part curing agent to 10 parts of the base silicone, specifically utilizing Sylgard 184 as the base material.
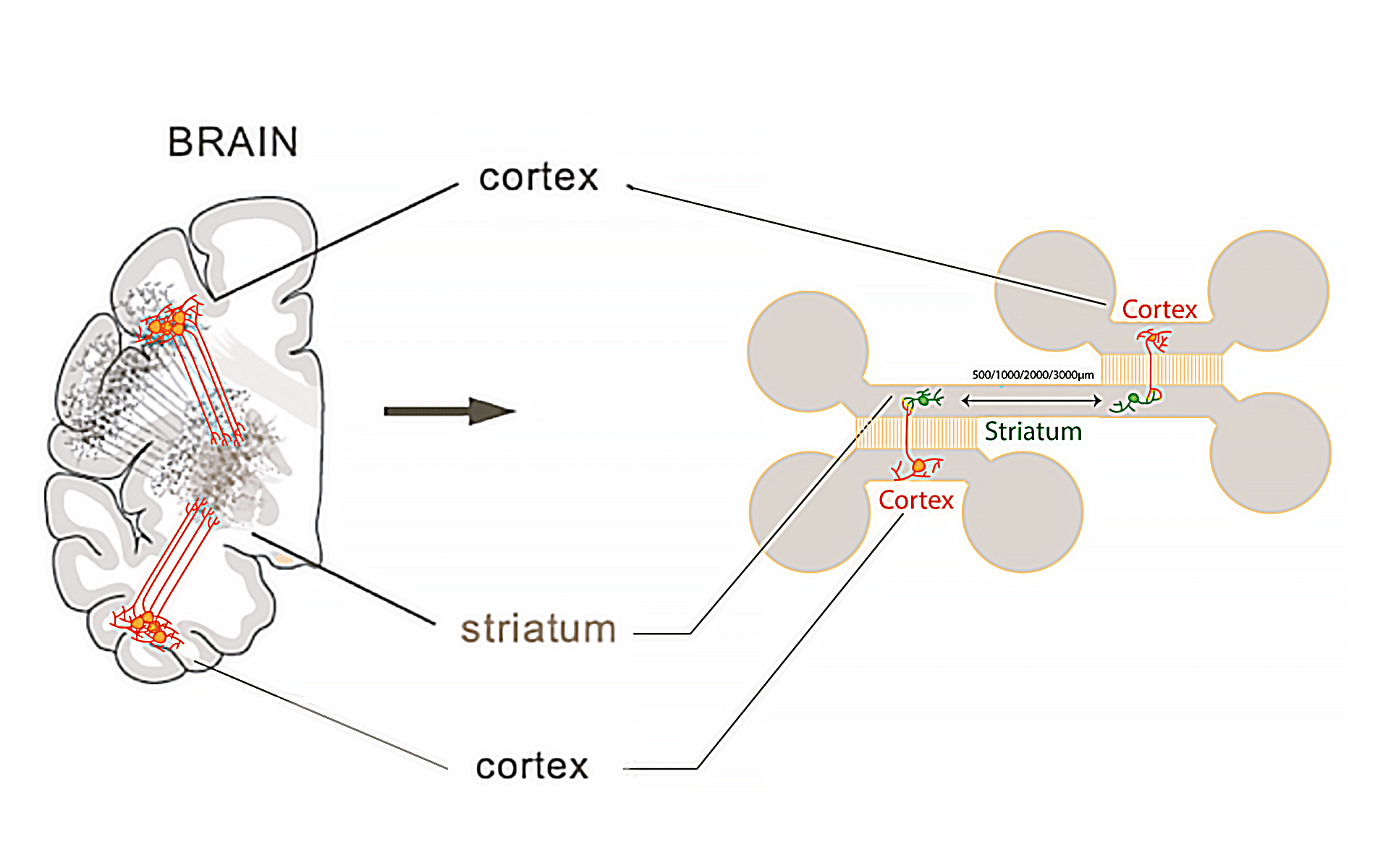
Automated protocol for neuronal cell immunofluorescence experiments
- Cell culture & preparation: After a culture period of 14 days, cells are fixed outside Aria system, in order to prevent contaminating the internal system with PFA/sucrose solution (flow unit, M-Switch).
- Neuronal cell immunolabeling using Aria: For this application note, a typical cell immunostaining protocol is used (Figure 2). After cells are fixed, the microfluidic chip is loaded into Aria, and the standard steps for immunofluorescence are followed: permeabilization, blocking, staining with primary antibody and secondary antibody, nuclei staining, and final wash.
- Imaging using microscopy: After completing the entire protocol, the microfluidic chip is disconnected from Aria and the neuron cells are ready for imaging. This protocol allows for efficient immunostaining of up to 12 microfluidic chips in a day, with minimal user intervention.
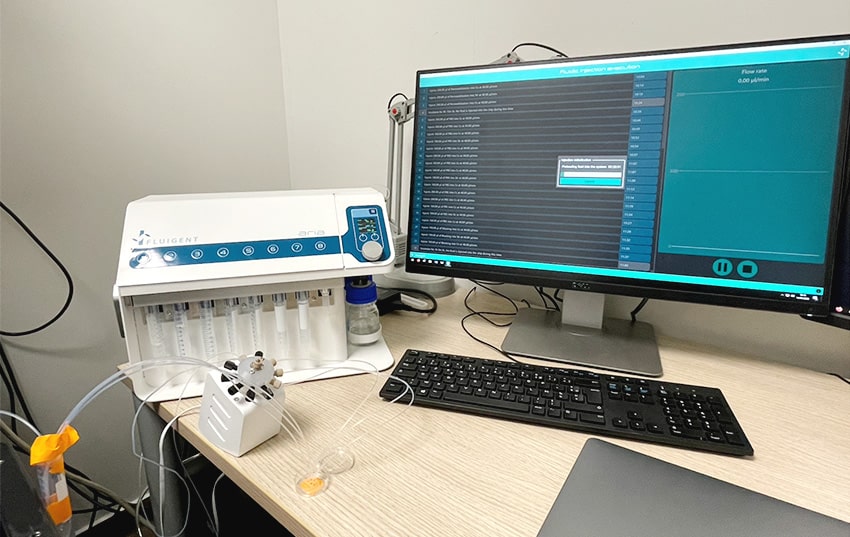
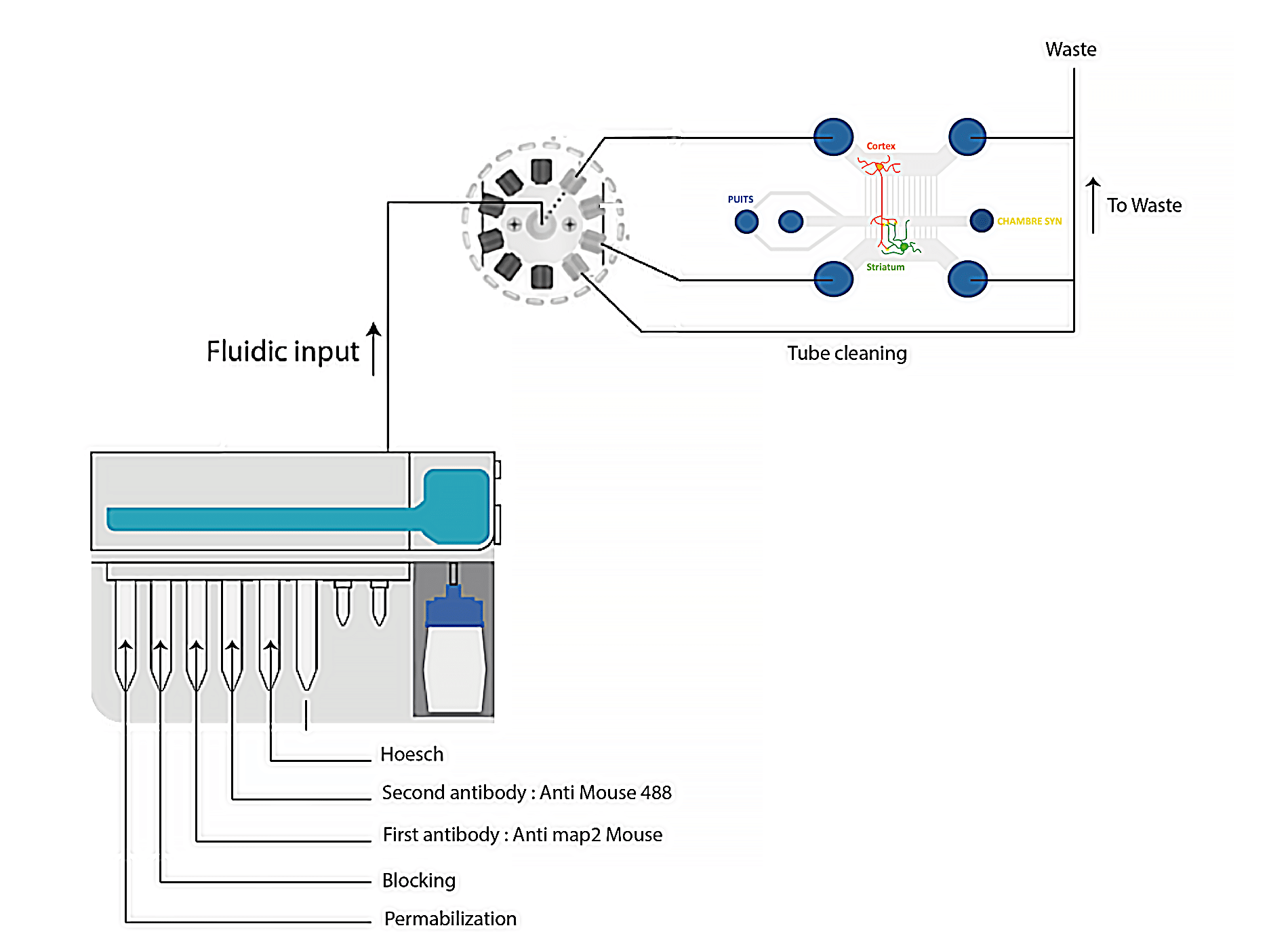

- Aria unit preparation: To initiate the protocol, connect the Aria unit to an external pressure source and ensure it reaches a minimum pressure of 2.2 bar. Connect Aria to your computer and place reagents in the specified reservoirs as per the software protocol. The user-friendly Aria software allows for easy calibration and custom protocol creation, offering precise control and smooth automation for neuronal cell immunofluorescence experiments to ensure accurate and consistent results while optimizing the use of Aria.
Results: Very clean cell staining
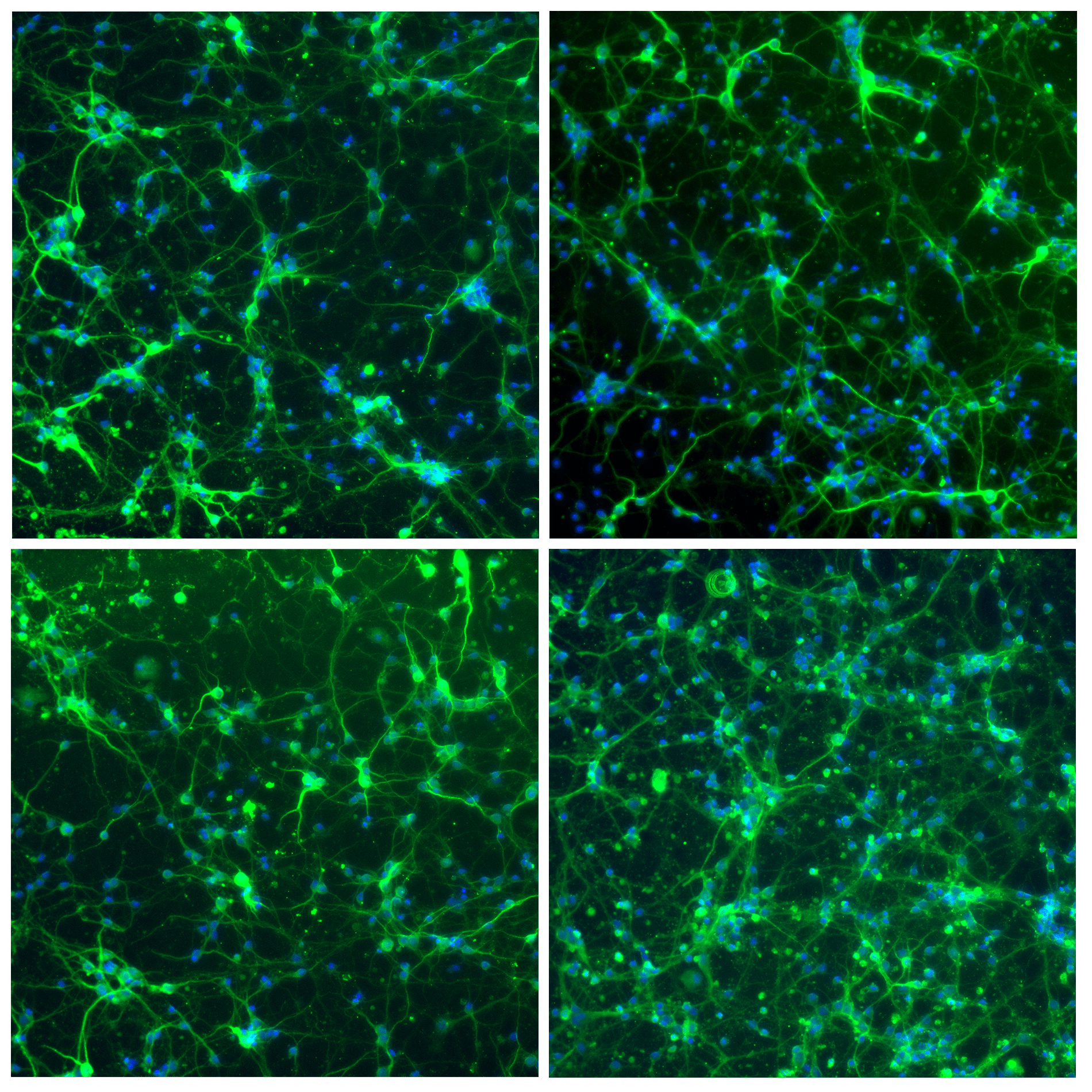
Figure 4 shows progenitor neuron cells inside the microfluidic chip, stained using the Aria system. Cells are stained for microtubule-associated protein 2 via the anti-MAP2 antibody (green), and for nuclei via Hoechst dye.
As shown in the figure, Aria makes it possible to achieve very clean cell staining while preserving the very delicate neuronal cell structures, including axons and dendrites.
Webinar – Automating Cellular Immunolabeling in Microfluidics
What you’ll learn:
- Introduction to Fluigent’s expertise in the field of microfluidics and Organ-on-chip
- Aria: Fluigent’s automated sequential injection system
- Success story using Aria for neuron immunolabeling
- Have a live discussion with our experts and the option to discuss specific applications
Conclusion & outlook
Aria significantly enhances the quality of neuronal cell immunostaining, eliminating the risk of manual errors and saving researchers valuable time. This innovation streamlines workflows, improves data reliability, and holds great potential for advancing our understanding of complex biological processes, particularly in the future study of axonal rewiring within microfluidic chips.
Related product
Platform for Spatial Omics
Read more11-port/10-position microfluidic valve
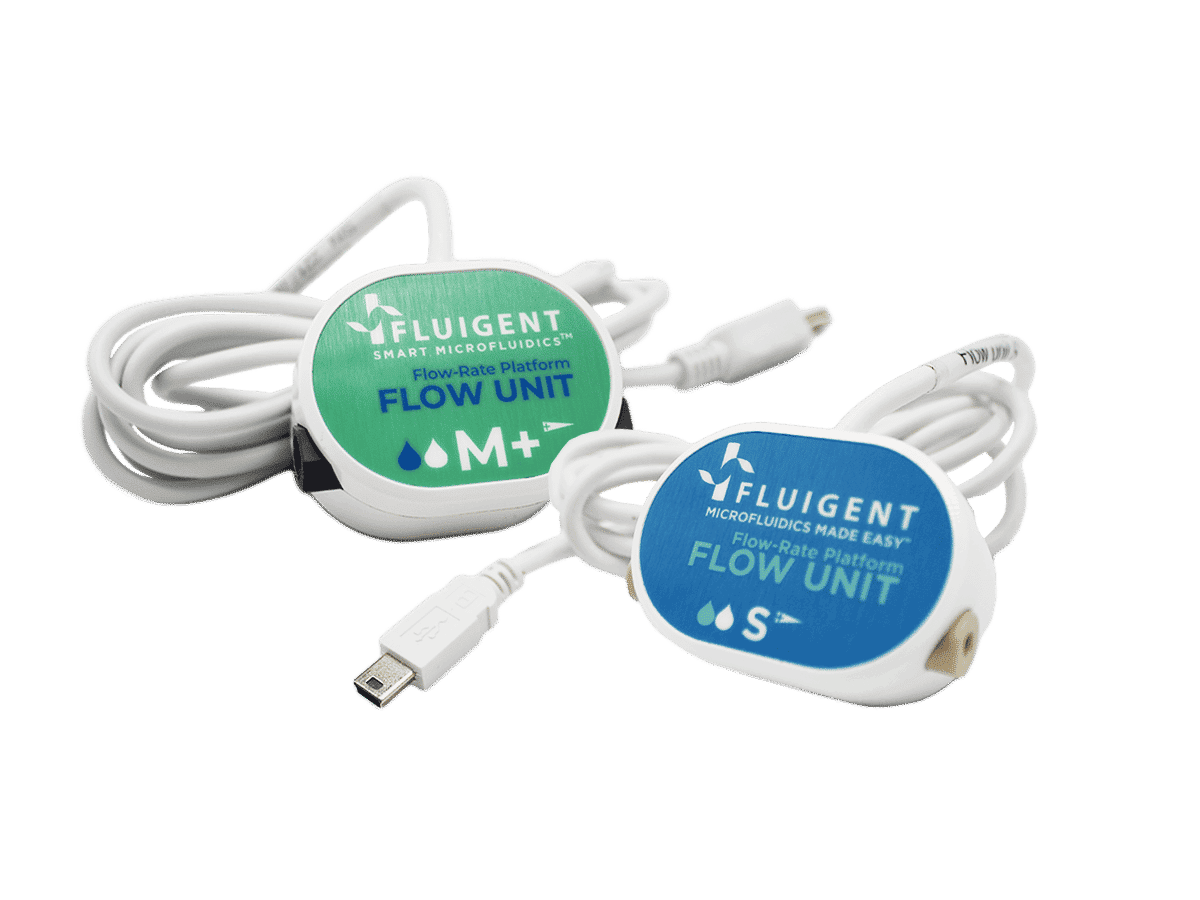
Read moreFLOW UNIT | FLOW UNIT +
Read moreMimic Microphysiological Conditions in Organ-on-a-Chip Studies
Read more
Expertises
-
Microfluidic Application Notes Automated Immunofluorescence using Aria Read more
-
Microfluidics White Papers A review of Organ on Chip Technology – A White Paper Read more
-
Expert Reviews: Basics of Microfluidics Why Control Shear Stress in Cell Biology? Read more
-
Microfluidics White Papers An exploration of Microfluidic technology and fluid handling Read more
-
Expert Reviews: Basics of Microfluidics Application of microfluidic chip technology Read more
-
Expert Reviews: Basics of Microfluidics Microfluidics overview: History and Definition Read more