Automated Immunofluorescence using Aria
In this Application Note, we introduce a cutting-edge Automated Immunofluorescence (IF) protocol that leverages the capabilities of the automated sequential injection system (ARIA) and the FCS2 imaging chamber. This innovative approach provides researchers with unprecedented accuracy and reproducibility in cellular and molecular biology imaging experiments. Read the application note and the technical note for more details.
Abstract
In this Application Note, we introduce a novel Automated Immunofluorescence (IF) protocol that integrates the advanced automated sequential injection system (ARIA) and Bioptechs’ FCS2 imaging chamber. This combination offers a breakthrough solution for researchers to achieve highly accurate and reproducible imaging results in cell and molecular biology experiments, providing a deeper insight into the intricate cellular and molecular interactions within the sample.
With this Automated IF protocol, the tedious and error-prone manual handling associated with traditional multi-step IF procedures is completely eliminated, resulting in a faster and more reliable process.
The application note was prepared in collaboration with Samy GOBAA (Director of the Biomaterials and Microfluidics Unit at the Pasteur Institute) and Heloïse Mary (Research Engineer at BMcf).
Introduction to Automated Immunofluorescence
Immunofluorescence (IF) is a widely utilized analytical technique in the field of cell and molecular biology, aimed at providing insights into the localization and distribution of specific proteins within cells, tissues, and organisms. The technique employs the use of antibodies, which can be conjugated with fluorescent markers or revealed through the use of secondary fluorescent antibodies, to target the specific proteins and enable visualization through the use of fluorescent microscopy. (1)
Automated immunofluorescence streamlines the multistep process of IF, which comprises several crucial steps, such as cell fixation, cell permeabilization, blocking of nonspecific binding sites, and direct or indirect staining, followed by several washing steps. The traditional approach to performing these steps has been through manual pipetting, however, this method is time-consuming and prone to inaccuracies due to human error in terms of solution volume and flow rate (2).
In recent times, there has been a growing emphasis on automating laboratory protocols to enhance the efficiency, accuracy, and reproducibility of results. Microfluidics has played a significant role in this advancement, by offering precise control of fluid flow and volume in complex analytical procedures such as IF.
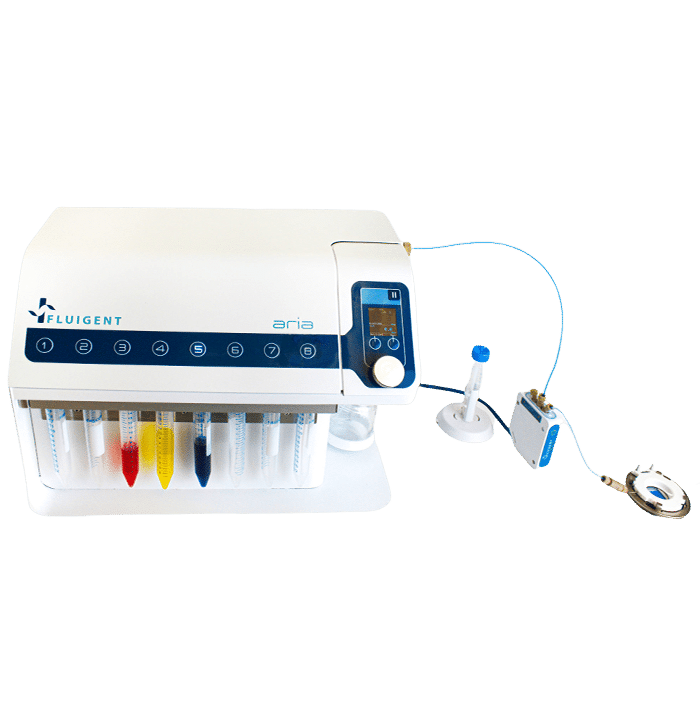
In this application note, we present an Automated Immunofluorescence Protocol that leverages the capabilities of the automated sequential injection system, ARIA, in combination with the imaging chamber FCS2 from Bioptechs. This protocol offers a marked improvement in terms of accuracy and reproducibility, compared to the traditional manual pipetting method, while also increasing the overall efficiency of the process.
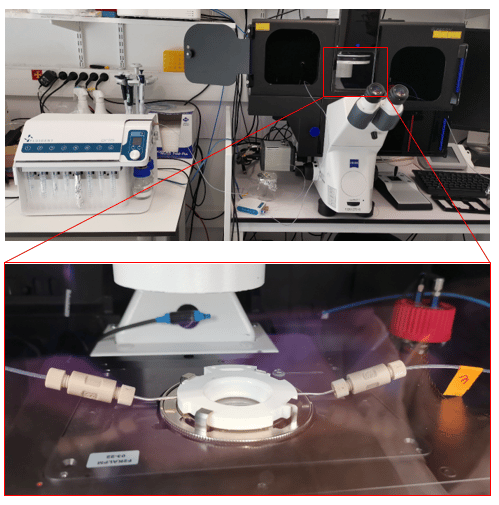
The fluid delivery procedure is coupled with the Zeiss Axio Observer for imaging purposes, although the protocol can be adapted to other imaging systems.
We are grateful to Samy GOBAA (Head of the Biomaterials and Microfluidics core facility at Institut Pasteur) and Heloïse Mary (Research Engineer at BMcf) for their contributions to this application note, including the provision of essential lab equipment and invaluable advice.
Materials & Methods: Immunofluorescence protocol
Materials:
- ARIA single output
- Bioptechs Live Cell Imaging Chamber (FCS2)
- Widefield Microscope (in this app note we used a Zeiss Axio Observer)
Methods :
To perform the automated immunofluorescence protocol, preliminary steps of cell preparation and FCS2 chamber preparation are necessary.
- Cell and coverslip preparation: Clean and coat round coverslips (40mm) with EtOH 70%, plasma, and collagen at 50µg/ml. Incubate for 1h @ 37°C. Seed HUVECs onto coverslips in EGM-2 medium for 1-2h to adhere.
- Fixation (manual or automated): Wash cells with PBS 1X, then fix with 4% PFA in PBS 1X for 20min. Rinse with PBS 1X to remove PFA.
- FCS2 chamber assembly: Mount coverslip on white part of chamber, hydrate with PBS 1X, close chamber, and place on microscope stage.
- Automated Immunofluorescence: Permeabilize with 0.1% Triton 100X in PBS 1X for 15min, wash with PBS, block with PBS 1X + 2% BSA for 20min, wash with PBS, and stain with a cocktail of fluorescent antibodies (DAPI, Phalloidin-AF488, UEA-1-lectin DyLight 647).
ARIA unit preparation:
To create a custom automated immunofluorescence program, ARIA needs to be prepared.
- Connect ARIA to pressure source (either a FLPG unit or directly on the wall pressure source), min. 2.2 bar and computer using USB cable.
- Open ARIA software and calibrate the unit.
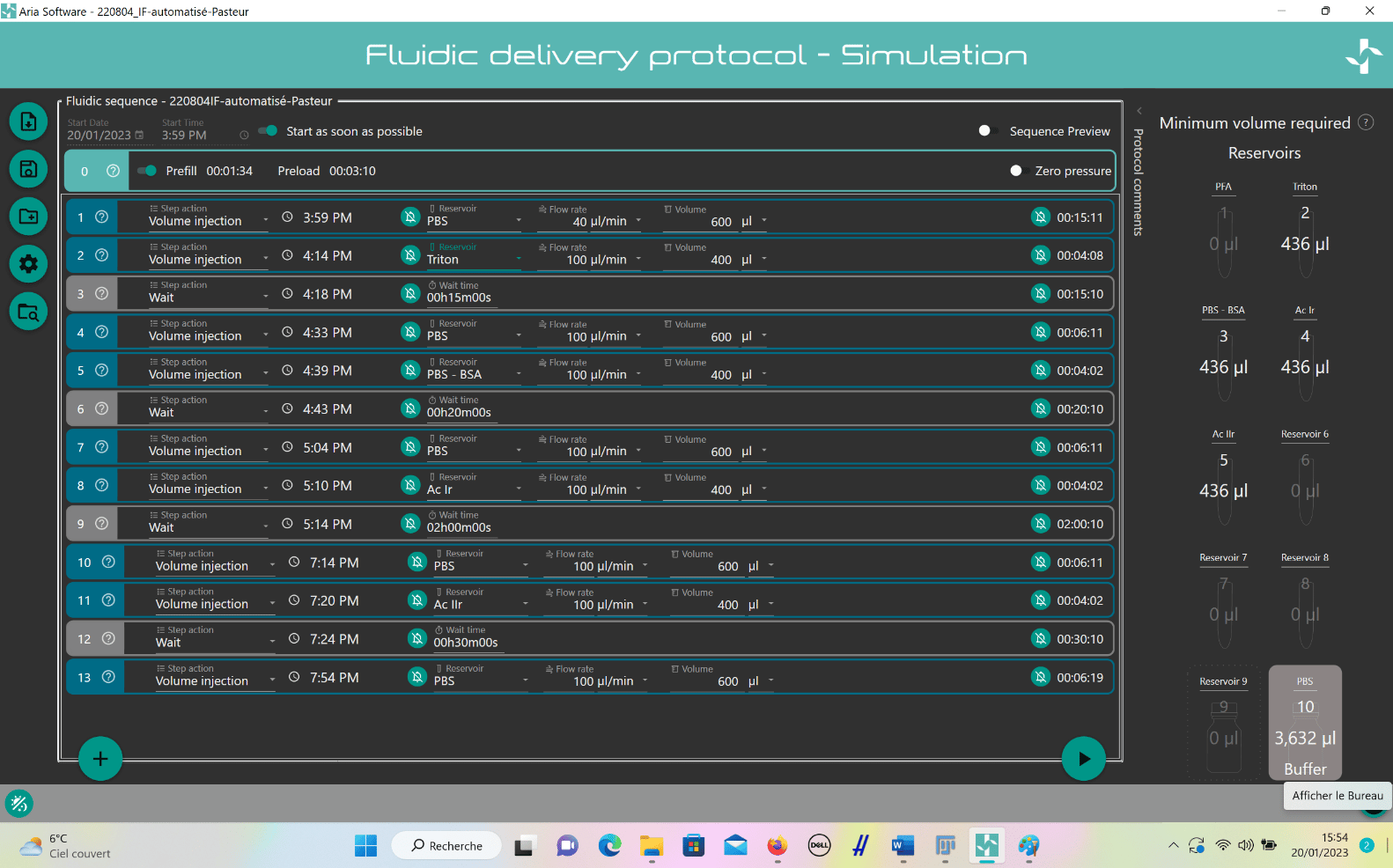
- Create custom IF program:
- Add steps by clicking “plus” button.
- For solution injection, choose “Volume Injection” and select reservoir.
- Set fluid delivery parameters (flow rate and volume).
- For incubation, add “Wait” step after injection and set timing.
- Repeat steps for entire IF protocol.
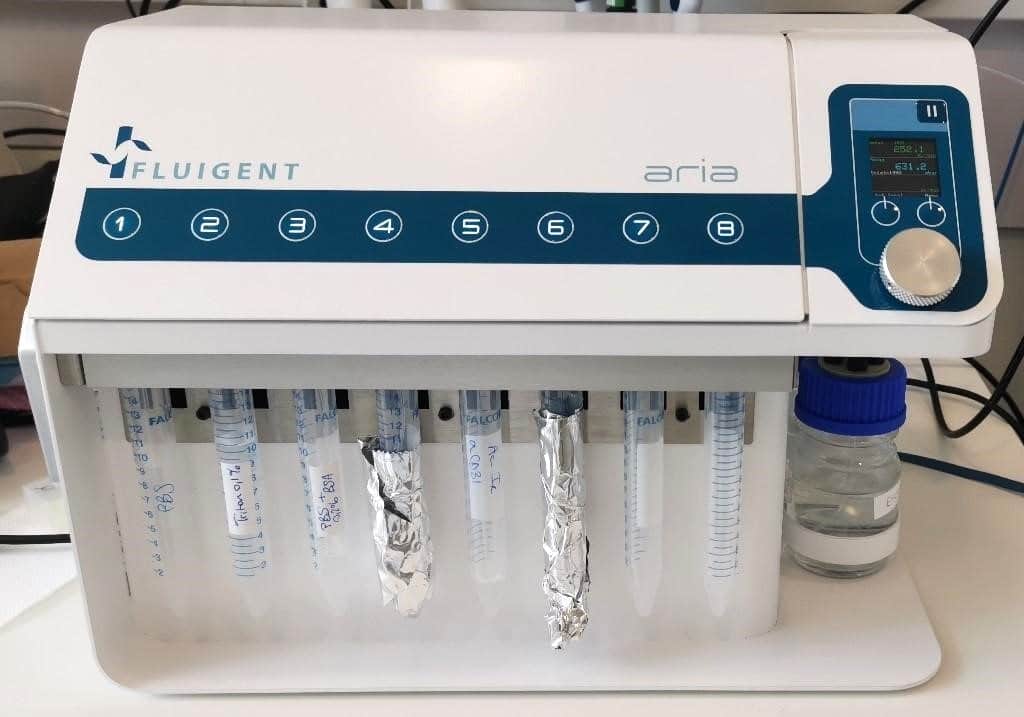
Results: Image acquisition
To acquire our images, we here used a Zeiss Axio Observer (inverted widefield microscope).
Please note that any microscope can be used to acquire your images as for any IF experiment.
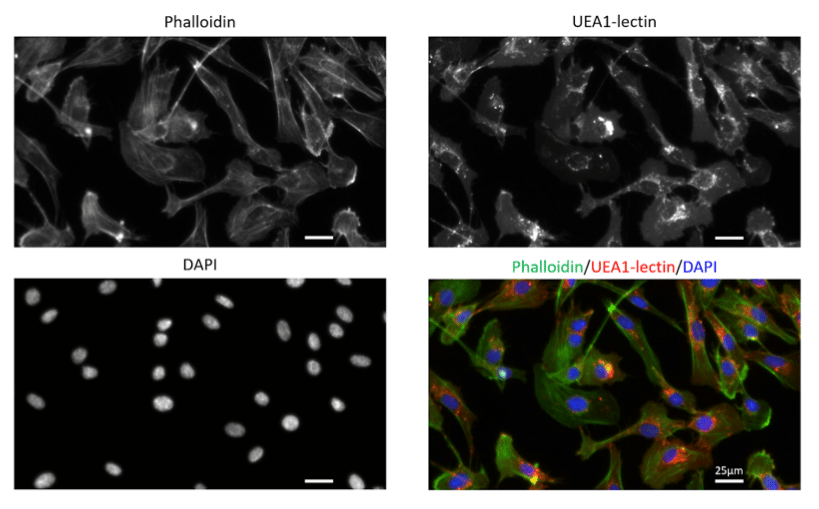
Figure 3. Primary human endothelial cells (HUVECs) stained with Phalloidin-AF488 for F-actin visualization, UEA1-lectin-DyLight as a membrane marker of endothelial cells and DAPI for nuclei staining. Images were acquired on a Zeiss widefield microscopy at 40X magnification.
Conclusion
This Application Note highlights the benefits of using the ARIA system and the FCS2 imaging chamber for automated immunofluorescence procedures. Our findings demonstrate that this method results in a faster and more efficient process, with a total time of 4 hours and 30 minutes. This is a significant time saving compared to traditional manual pipetting, which can take up to 1 hour and 30 minutes longer.
The automation of this process allows researchers to perform other tasks simultaneously, freeing up valuable time and resources. Furthermore, this protocol is versatile and can be applied to cells on coverslips and cells or tissues in microfluidic chips, making it a useful tool for cell and molecular biology research.
References:
- Im K, Mareninov S, Diaz MFP, Yong WH. An Introduction to Performing Immunofluorescence Staining. Methods Mol Biol. 2019;1897:299-311. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-8935-5_26. PMID: 30539454; PMCID: PMC6918834.
- Lim, Jeffrey Chun Tatt & Yeong, Joe & Lim, Chun Jye & Ong, Clara & Wong, Siew-Cheng & Chew, Valerie & Ahmed, Syed & Tan, Puay & Iqbal, Jabed. (2018). An automated staining protocol for 7-colour immunofluorescence of human tissue sections for diagnostic and prognostic use. Pathology. 50. 10.1016/j.pathol.2017.11.087.